Genetic links to fear response shed light on cattle temperament
Study is first to analyze beef cattle temperament using whole-genome sequencing.
August 27, 2020
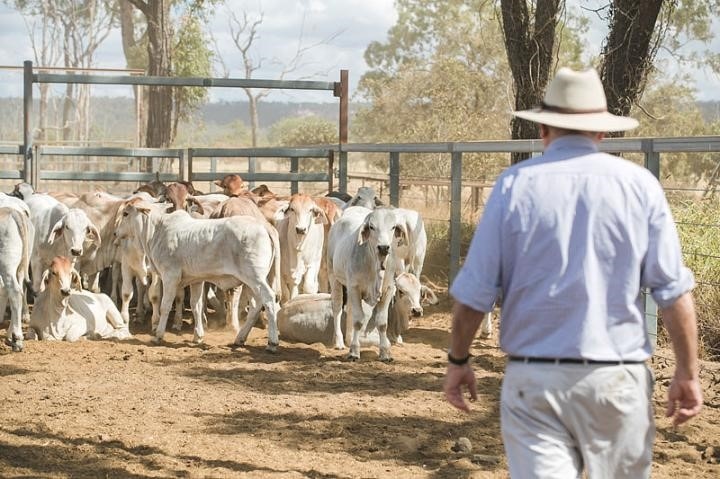

A strong association between the genes influencing cattle temperament and autism in people has been discovered by researchers with the University of Queensland (UQ) in Australia. UQ genomic expert professor Ben Hayes said the research by his interdisciplinary team, headed by Dr. Roy Costilla, could lead to improved animal welfare and meat quality.
"The research doesn't mean that cattle have autism, [but] rather, that cattle share an overlap of genes with humans that are critical in brain function and response to fear stimuli," Hayes said.
Temperament is an important trait for day-to-day management of cattle.
"We knew that genetic factors were likely influence temperament in cattle, and we thought that genes involved in behavioral traits in humans could also influence temperament in cattle," he said. "We found that genes known to contribute to autism spectrum disorders also influence temperament in cattle."
Hayes said the outcome was important because it opened the way for research conducted on behavioral traits in humans to shed further light on temperament in cattle.
"As I've found talking to farmers over the years, it can be distressing having an animal that has a poor temperament in the mob and stirs up all the other cattle, putting them into a state of stress," Hayes said. "If we can identify those animals early or breed to eliminate them, we can potentially reduce the stress of the whole mob.
"That has great implications for welfare — not only of the cattle but also the people handling the cattle who are less likely to be charged or kicked," he added.
Hayes said there was an association between a calmer temperament in cattle and better meat quality.
"The cattle industry's standard for measuring temperament is 'flight time' — the speed in which cattle move after release from an enclosure. What a producer wants is cattle that move calmly and slowly from the enclosure, rather than an animal that charges out in an aggressive or stressed state," Hayes explained.
"Our study found flight time is about 35% heritable, which is very significant," he said. "It means you can make a lot of progress by breeding for better temperament; it's about the same as milk production in dairy cattle, and we've made big breeding gains there."
Hayes said the same genes were identified in other genomic research conducted on domestication of foxes.
"The same genes just come up again and again," he said. "Some DNA variants in those genes are more common in people with autism, and in cattle, some DNA variants in those same genes are found to make the cattle more fearful in new situations and have a reactive temperament."
UQ noted that the study is the first time whole-genome sequencing has been used to analyze temperament in beef cattle. The researchers looked at 28 million data points per animal for the 9,000 cattle with temperament records in the initial study and then validated the results in more than 80,000 cattle from Ireland.
Hayes said his team would incorporate the temperament data into a panel of markers available for producers that would also provide breeding values for fertility.
"It means a producer will be able to use a sample of tail hair that contains DNA to quickly get information on the genetic value of their animals for temperament and fertility. The temperament analysis was conducted primarily in northern cattle Bos indicus breeds and was validated in Bos taurus cattle," he said.
The study was a result of cooperation among Australian researchers, the beef industry and international collaborators from Ireland and Brazil.
The research was published in Genetics Selection Evolution.
You May Also Like