Self-powered water quality sensor could help fish farmers monitor pollution in ponds remotely.
February 27, 2020
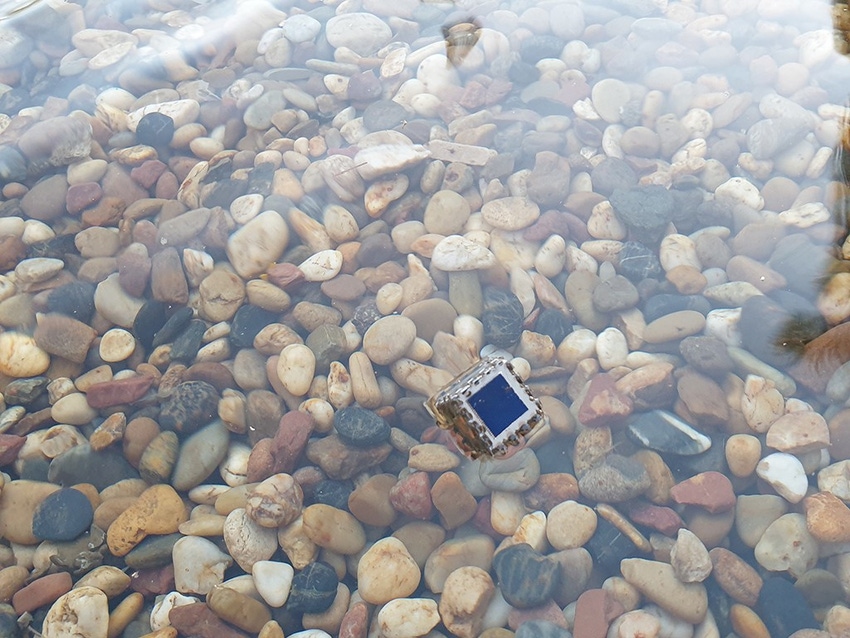

Solar-powered water quality sensors could help fish farmers protect their aquatic assets and safeguard the future of food, according to an announcement from King Abdulla University of Science & Technology (KAUST) in Saudi Arabia.
Aquaculture currently supplies more than half of the world’s seafood, and in the last 10 years, the profits from global fish farming have quadrupled to more than $230 billion annually, KAUST said.
By keeping an eye on water quality, fish farmers can act when harmful levels of pollution are detected. However, most commercial sensors only monitor one thing at a time, such as acidity or oxygen levels, on individual devices that the farmer must check manually, KAUST said. The multifunctional alternatives are bulky, expensive and need an expert operator.
Creating electronic devices that do several things at once is challenging, and there is often a trade-off between quality and the quantity of functions, KAUST said.
KAUST electrical engineer Muhammad Hussain and his team created a small self-powered sensor that monitors multiple water quality characteristics and transmits the data via Bluetooth. The researchers built this system using a multidimensional integrated circuit (MD-IC).
“Integrating different functions on to one computer chip is complex and expensive,” lead author Nazek El-Atab explained. “We have combined several chips into a cube so that each face serves a different purpose.” The connected chips then act as one device.
The cube is designed to float with the sensors for pH, temperature, salinity and ammonia levels on the downward-facing side. The casing is weighted to ensure that it remains that way, even when disturbed by fish. "We wanted to create something small and lightweight,” El-Atab said. “The farmer can simply throw the device into the water, and it rotates itself into the right position.”
The other outer faces include sensors that monitor air pollution, solar cells to charge the battery that is sealed within the cube and an antenna for transmitting data via Bluetooth to a mobile phone, KAUST noted.
“The concept of MD-ICs is unique, as it opens up opportunities for single devices with Internet of Things applications,” Hussein explained. “Water is always an intriguing medium for electronics.”
Preventing unnecessary fish deaths is a crucial step toward food security.
“Saudi Arabia is investing $3.5 billion (U.S.) in aquaculture so it can produce 600,000 tons of seafood each year by 2030,” El-Atab said. The team hopes its sensors will support this goal but also believes the little cubes could have a big future beyond the fish farm. "They could be sent down oil pipes to collect data on oil quality,” she added.
The researchers are working on improving the device’s self-cooling technology to stop it from overheating, and the next step will be to test it in the field.
The research was published recently in the journal Small.
You May Also Like
.png?width=300&auto=webp&quality=80&disable=upscale)
